Subsections of Linear Modifications
About Linear and Boolean Modifications
This set of commands mostly applies to linear objects with the exception of boolean operations that apply to polygonal shapes.
Topics in this section
- Mark Intersections
- Join
- Extend
- Split
- Trim
- Divide into Parts
- Break
- Boolean Operations
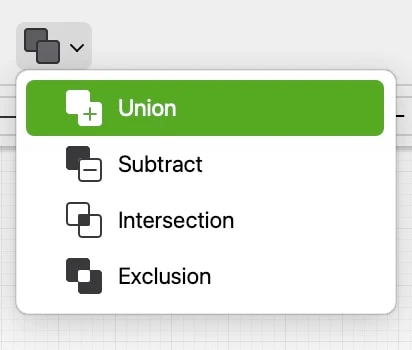
Boolean Operations
Boolean operations combine two polygons using one of the following intersection formulas:
- Union: combines the two polygons together to form a new polygon. The internal intersections are ignored and only the maximum external profile is used to define the new shape.
- Subtract: uses the second polygon as a “clipping” shape to remove the intersecting area from the first polygon.
- Intersection: creates a new shape by the intersection of the two polygons and discards the outer perimeter.
- Exclusion: the opposite of Intersection, it shows only the areas of the two polygons that do not overlap.
▶︎ Boolean operations must be applied to linear polygons: rectangles, regular polygons, hatches, polylines with straight segments.
▶︎ The order of selection matters: the first object selected acts as the base shape and the second object as the clipping shape. The polygon resulted from the boolean operation inherits the properties of the base object.
Break
Use this tool to define a segment that will be subtracted from a selected object. The command applies to lines, polylines, arcs and circles, and walls.
Select Drawing ▸ Break, click on a line to set the first point of the segment and click again to set the endpoint.
Applies to:
- Selected object
Steps
- Select the object and activate the command.
- Click on the object to define the first break point.
- Click to define the second break point.
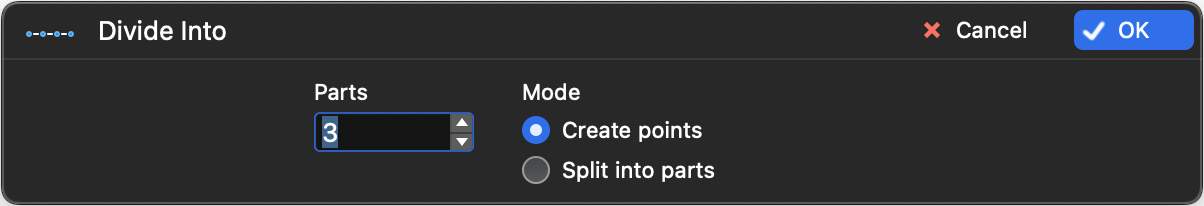
Divide into Parts
This command is used to divide the selected line into the number of equal segments you specify in the Divide Into dialog. This dialog lets you also choose whether divide the line with alignment points or actually create segments.
The command applies to lines, polylines, rectangles, polygons, arcs and circles.
Applies to:
- Selected objects
Steps
- Select the object
- Activate the command
- Enter the desired number of parts and select the division mode. Push OK.
The Divide Into dialog can be used via the keyboard: the Up and Down arrow keys control the number of divisions; Command + Up/Down arrow controls the option buttons.
Extend
This function extends the selected lines (either by lengthening or shortening) to their intersection point with another object. Supported types are:
Construction line, Line, Polygon, Rectangle, Spline, Bézier curve, Arc / circle, Wall.
Applies to:
- Selected lines or walls
Steps
- Select an object
- Activate the command
- Click on the destination object
Join
This command connects two linear objects so that they either intersect on one point or form a new object. Lines and walls, being individual objects, intersect; polylines, paths and splines are joined together to form a new object.
The Join command applies to:
- Two lines
- Two walls
- A line and a polyline
- Two polylines
- Two bezier paths
- Two splines
This command does not apply to two different classes of curves, or a spline and a polyline, or two parallel objects.
Applies to:
- **Applies to: **selected objects
- Steps: direct command
Steps:
or
or
- Select an object
- Apply the command
- Click on the destination object
This second method allows you to join objects in sequence.
Mark Intersections
This function finds all possible intersection points between two selected items. The points are marked by simple alignment points created on the current layer and with the default pen color.
This command applies to lines, polylines, rectangles, regular polygons, hatches, curves, and walls.
Applies to:
- selected objects
Steps:
- Select two objects. The objects do not need to intersect each other.
- Apply the command.
Split
This function splits linear objects into segments using another object as “cutter”. The Split command applies to lines, poly-lines, rectangles, arcs, circles, freehands and bezier curves.
Rectangles and polygons are transformed into polylines after the split.
Applies to:
- Selected oobjects
Steps
- Select the object to split
- Activate the command
- Click on the “cutter” object
Trim
The Trim function is a multipurpose function designed to delete linear or curved segments or parts. It applies to single segments without intersections with other objects as well as to segments intersected by other objects.
Segments without intersections
Activate the tool and click on the segment to delete: if the trimmed segment belonged to a rectangle or polygon, the remaining segments are turned into poly-lines.
Segments intersecting other objects
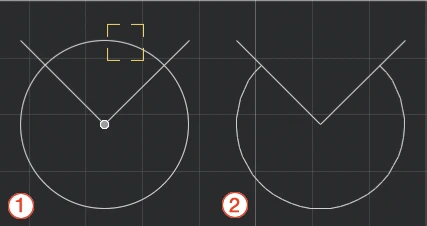
Activate Trim and click on the segment or part of segment to delete: use this tool to clear a drawing and cut segments, arcs and curves between intersections or extending off an edge with just a click.
To apply it:
- Choose Drawing ▸ Trim or click on the corresponding icon of the Edit Tool Bar;
- A visual aid highlights the segments under the pointer (1);
- Click the parts of the objects you want to trim;
- All segments and portions of arcs between intersections or extending off the edge will be deleted (2);
- Click an empty region to quit this command or press the Esc key.
You can also activate the Trim command by holding down the Backspace or Canc keys on the keyboard and clicking the object, or by clicking with the eraser tip of a graphic pen. No selection is required to use this function.
When activated with a selection, the selected objects acts as “cutters” and control the intersections. All intersections that do not belong to a selected object are ignored.
Applies to:
- objects at click
Steps
- click on the destination objects