Subsections of Architectural Design
Columns
Subsections of Columns
About Columns
Columns are vertical elements of the building with a structural function. They vary in shape and size, and share some of the properties of walls.
Topics in this section
- Column Tool Settings
- Place a column
- Editing columns
Column Tool Settings
Double click the Column tool icon on the Toolbox to open its Settings panel.
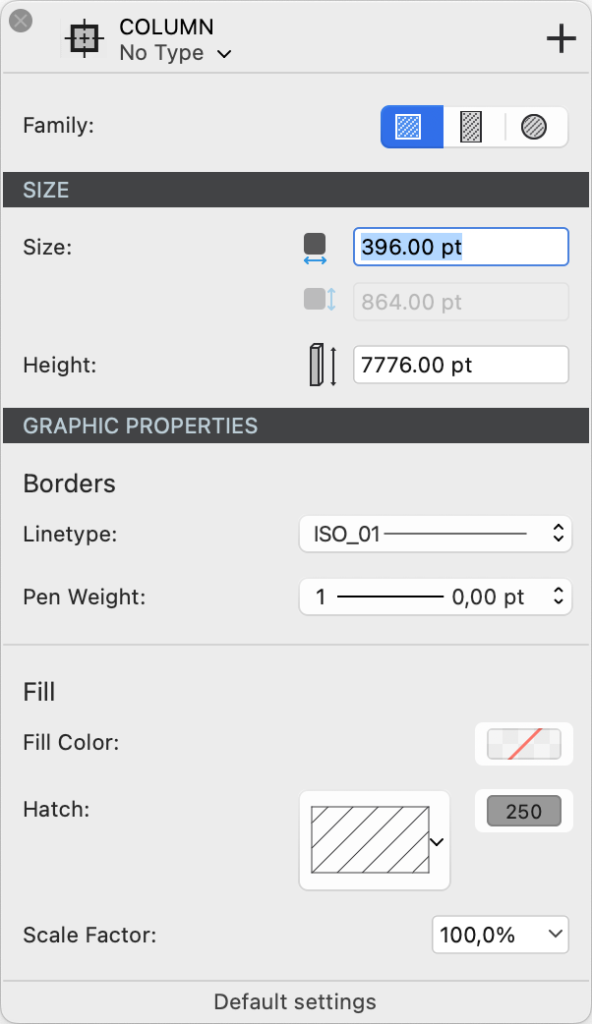
The panel is organized into three sections to define the column’s family, dimensions, and graphic attributes.
Family
A column’s family is defined by its shape. Click the desired shape choosing from Square, Rectangular and Circular.
Dimensions
You can define base width, base height and height of the column. The base width field is always enabled and in the case of a circular column it defines the diameter of the column.
The base height field is only enabled when the current family is Rectangular column.
The Height field is used for the total height of the column from the base level.
Graphic Attributes
The Graphic Attributes section is divided into two sub-sections: Borders and Fill.
Borders
You can define the line type and the pen weight of the border line of the column in plan view.
Fill
You can add a fill to the column and define:
- A solid fill color
- A vector hatch or pattern and set its color and scale factor.
The fill can use either one of the two fill modes or a combination of the two.
Editing Columns
Move a Column
- Select the column and click its center point.
- Move to the desired location and click to confirm.
Resize
To resize a column, you can use the Column Tool Settings panel, or the Object Info panel.
Editing with the Column Tool Settings panel:
- Select the column and open the Column Tool Settings panel.
- Change the family if you want to reshape the column, or enter the new base width and base height values.
Editing with Object Info:
- Select the column
- Enter the new values for base width, base height and column height.
Place a Column
Before placing a column, choose its type or set is shape, size and graphic attributes in the Column Settings panel.
Columns are always inserted by their central point, so that they align correctly to the structural grid.
- Round columns are inserted with a single click.
- Square and rectangular columns (pillars) require two clicks:
- click to define the center or insertion point;
- move the pointer and click a second time to define the angle of the column. Use the Angle input (A) to enter the desired value.
Alignments
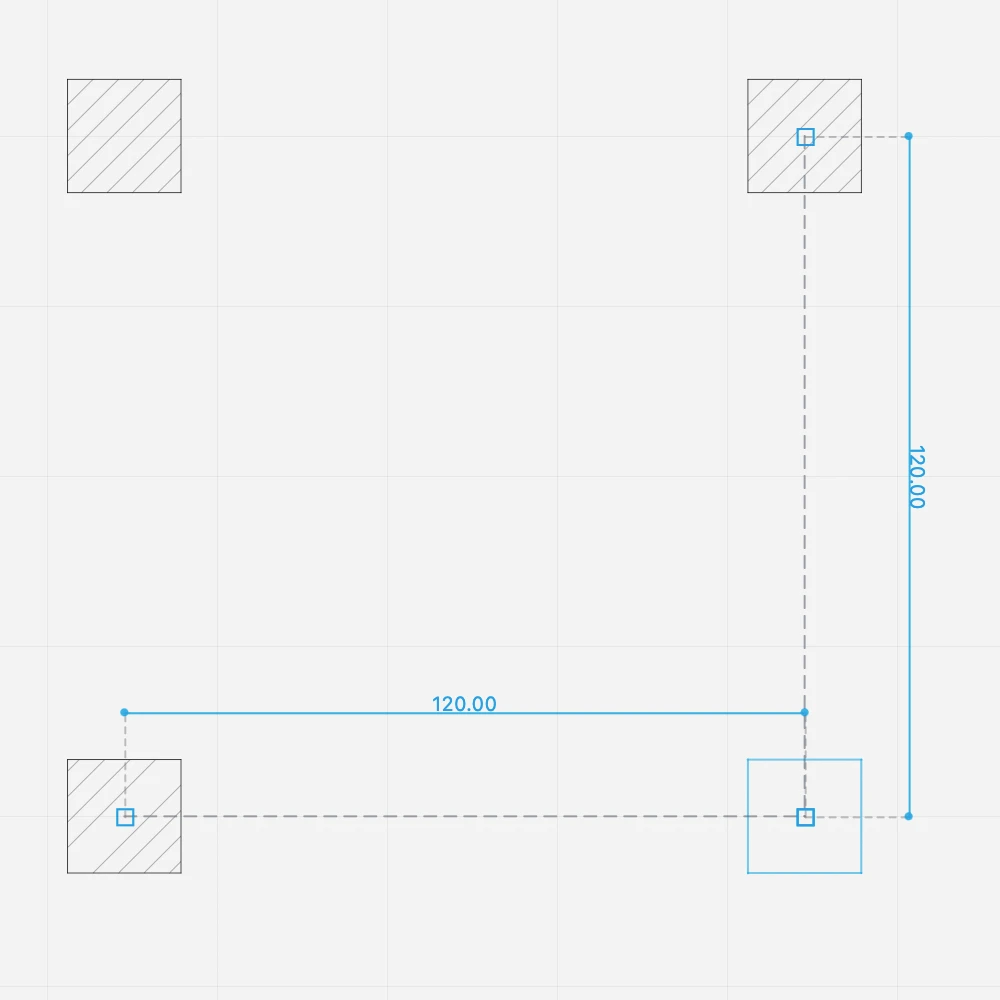
When you insert the second column, it automatically aligns with the first column so that you can create the structural grid by placing the columns with just one click.
Square columns also inherit the same orientation as the first column. To change the orientation, hold down the Alt key when you insert the column.
To place a column at a fixed distance:
- If not already active, press the Column tool button on the toolbox to activate it.
- As you move the pointer, dimension lines show the distance from the nearest column.
- Enter a distance and press Return or Enter.
The next columns will align to that orientation and snap to the predefined distance.
Doors
Subsections of Doors
About Doors
Doors are, like Windows, architectural elements that belong to the Openings class and in their most basic function are used to open holes in walls. Openings are hosted elements in that they can only be placed in a wall that acts as the host element.
Like any other architectural element, doors have geometric, graphic and information parameters that you can edit through the settings window and the Object Info panel.
Topics in this Section
- Door Tool Settings
- Insert a Door
- Editing a Door
Door Tool Settings
To open the tool settings of doors, select Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Door… or double-click the tool icon. You can load an existing Door Type if available or customize the door by selecting its family and setting all the parameters and options. Current settings can be saved as new types by pressing the Add icon.
The Door tool settings window includes two panels: Geometry and Options.
_
Door Geometry
Use this panel to configure the parameters that define the shape and size of the door, such as width, height, reveal type, etc. The panel is provides the following options:
- Family. Open the drop-down menu to select the door family from the list. The available families include:
- empty opening
- simple door, a symbolic representation of a door
- swinging doors
- bypass sliding doors
- surface sliding doors
- pocket doors
- folding doors
_
Door Options
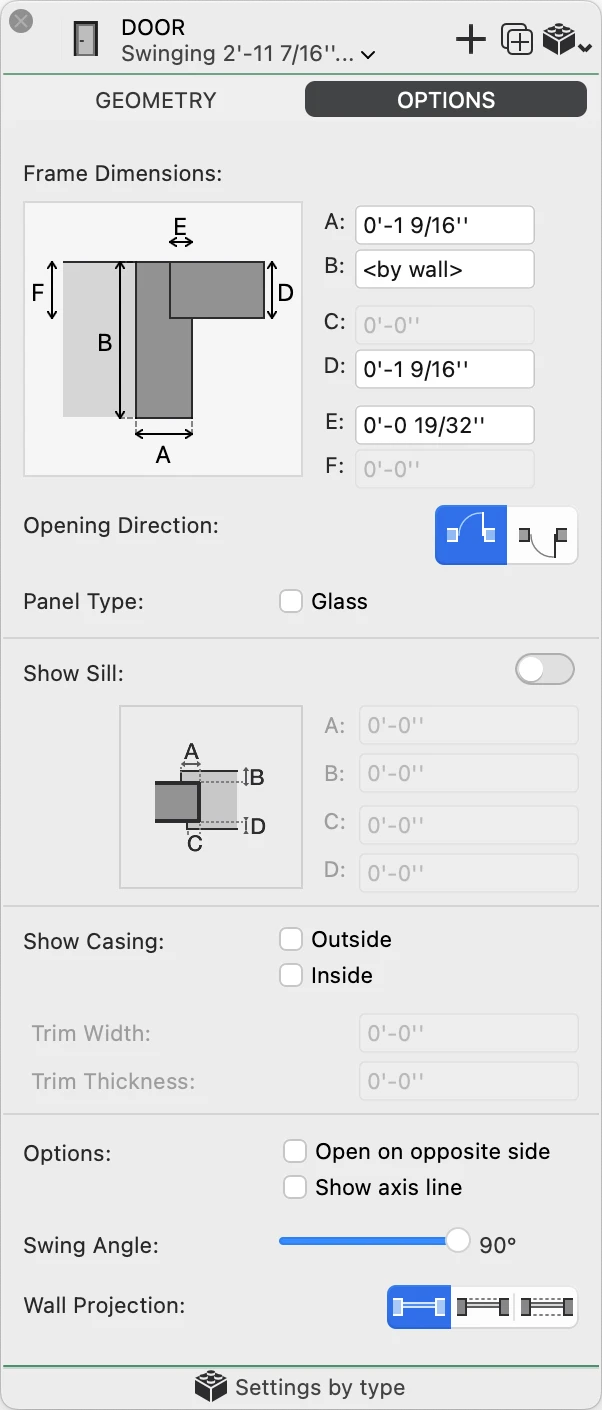
Use this panel to specify the dimensions of the frame, opening directions, the optional sill and various display options.
Door Options
Use this panel to specify the dimensions of the frame, opening directions, the optional sill and various display options.
- Frame Dimensions. Depending of the current reveal, you can specify the dimensions of the various components of the door frame.
- Opening Direction, outward or inward.
- Panel type. Select Glass to add a glass to the internal panel of the door.
- Show Sill. Activate the switch to enable the controls and define external and internal offsets and widths of the sill.
- Show Casing. Depending on the desired level of detail, you can choose to display the outside and inside casing component and specify its dimensions.
- Display Options:
- Select Open on opposite side to flip the opening direction.
- Show an axis line on the middle of the opening.
- Define the angle at which swinging door are displayed, ranging from 0° (closed door) to 90° (fully open).
- Wall Projection. Choose whether to display one, two or no projection lines of the host wall.
Editing a Door
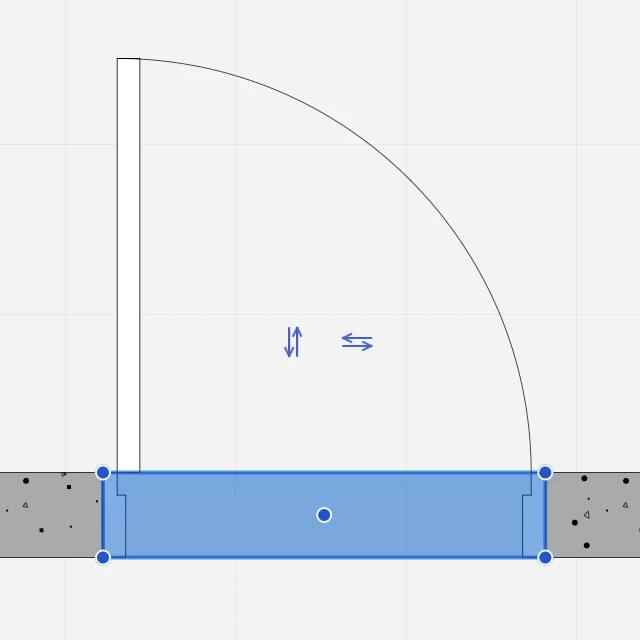
You can resize, move and flip a door directly by clicking one of its control points. All editing operations are available when the door is selected, but the flip operations are only available when the door is the only selected object.
Resize a Door
To resize a door, click one of its handles at the start or end sides and move the pointer. Pop-up dimensions show the current size. You can enter a new size value or click to end the editing operation.
Move a Door
Click its middle handle to move the door within its wall.
Flip a Door
Click the double arrows to flip the opening direction, outside or inside, and the swing side, left or right.
Edit a Door with the Object Info Panel
You can also use the Object Info panel to resize the door.
The Geometry section displays the Rough Width and Nominal Width fields to change the size of the selected door.
The ID section shows the Name, Tag and Description fields to edit or add information to the selected door: use the Settings button to open the Door Settings window for specific editing options.
Insert a Door
To insert a door in the project follow the steps below:
- In the Settings window load the Type if available or select the family of the opening;
- Alternatively, define custom door settings;
- In the Project window set the position of the opening by clicking on the wall;
- Click the internal / external area of the wall to choose the opening direction;
- For single doors (swinging, sliding, pocket or folding doors) click on the wall to position the door, then click in the desired quarter of the region described by the cartesian axes to set its opening or swinging side. As you move the cursor over a wall, temporary dimensions show the relative distances of the door from the surrounding vertices or joints of the wall. As for windows, to set and constrain the value of either dimension, so that the opening is exactly at that distance from a reference point, enter the value on the keyboard and move the pointer, so as to choose which dimension on either side of the wall the value applies to. Click to confirm and insert the opening.
Walls
Subsections of Walls
About Walls
The Wall tool allows the creation of walls which are parametric objects, automatically connected on their vertices and borders. To set the attributes, double-click the Wall Tool icon or select Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Wall… to open the Wall Settings dialog.
Walls are host elements, in that certain elements like doors and windows can only be inserted in a wall.
Walls are classified into two families: Standard-case Wall, made of one, uniform component, and Composite Wall, made of different internal components.
Topics in this Section
- Wall tool settings
- Standard-case Walls
- Composite Walls
- Construct and Edit Walls
- Utilities for Walls
Compound Walls
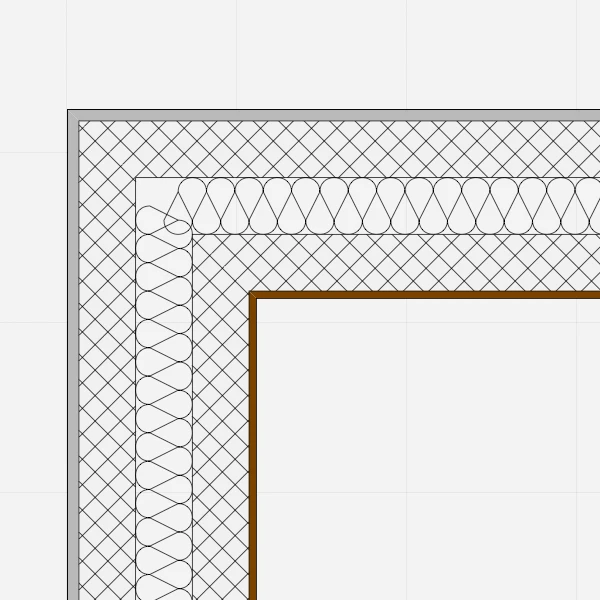
Compound walls consist of multiple layered components, each with its own properties. Compound walls can only be rectangular in shape, with constant thickness from start to end. The total thickness is calculated as the sum of all the internal components.
_
- Compound walls can have any number of internal components, and you can add, remove, reorder and edit the components at any time through the Components window.
- By default, basic walls and compound walls do not join automatically, because they are different elements that would not be joined in a real situation. Also, they are made of different materials which would not match. However, if a particular situation requires it, you can choose to activate the Allow Joints options and attempt to join two walls of different type.
- Compound walls can use one pen weight for both borders and internal divisions, or you can assign a pen weight for the outer borders, and one for the internal components.
_
Compound Wall Settings Window
- Type pop-up window and New Type icon. This window lists all the available Types, of both basic and compound families. It is advisable to enter descriptive names when saving a new wall type.
- Wall Family.
- Components section:
- Edit Components button to access the Components window; use this button set the components of a new wall or edit an existing wall.
- Total computed thickness; the sum of thickness of the internal components determines the total thickness of the wall.
- Internal pen weight of components. The pen weight can be Same As Borders to set the same pen weight as that used for the borders of the wall, or one of the available pen weights.
- Leading Side: see Basic Wall Properties Window for the description.
- Wall Joints options: see Basic Wall Properties Window for the description.
- Border line type and pen weight. Internal components can only have a continuous line division.
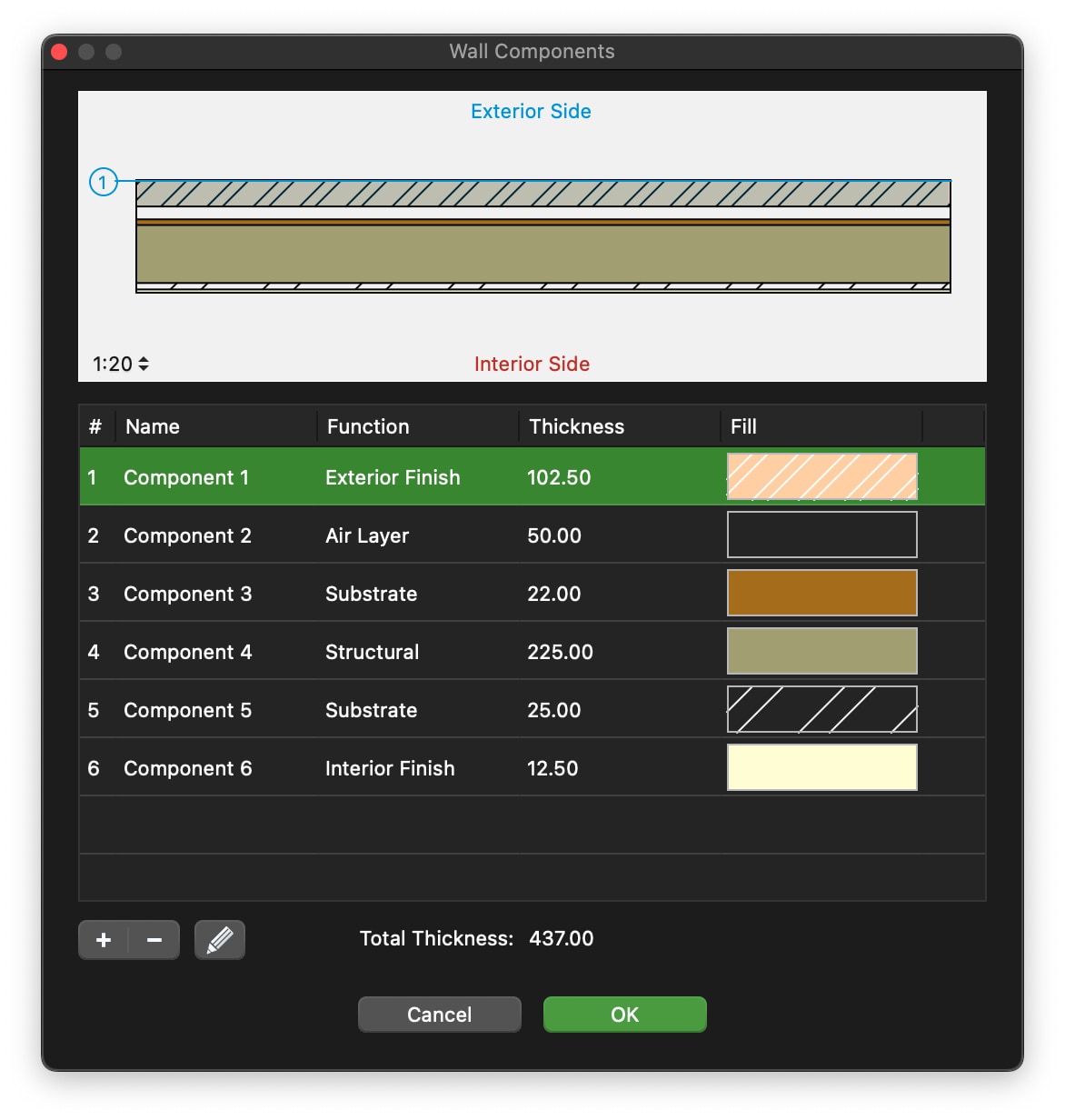
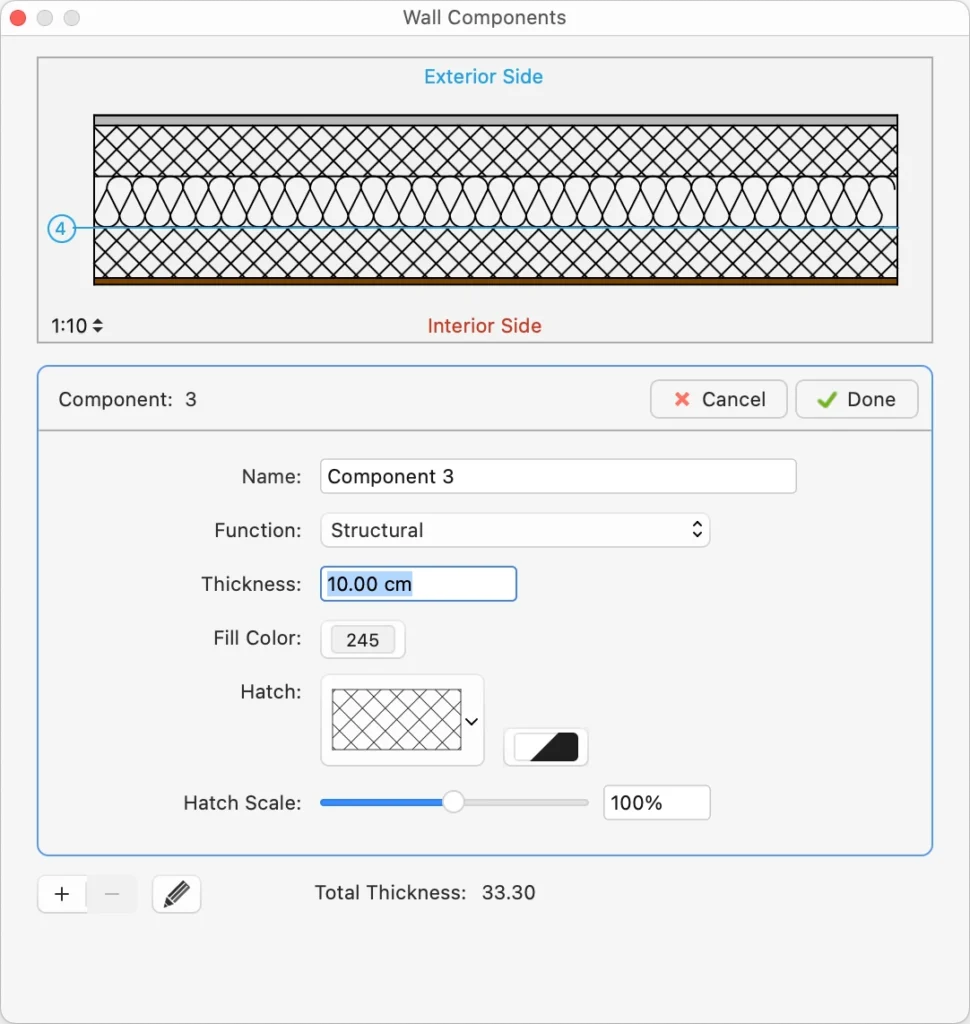
Wall Components Window
Use this window to set and edit the components of a compound wall.
The table lists the components of the wall from the exterior side to the interior, with a progressive index number. The selected component is highlighted in the preview, which shows the current wall at the scale set in the lower left corner. You can check how the wall is rendered at the different drawing scales by using the drawing scale menu.
The total thickness of the wall is computed on the sum of the single components and shown at the bottom of the Thickness column.
You can add, remove and reorder the components, and rename a component by double- clicking its name. Use the + button to add a new component and the - button to remove the selected component in the table. Adding a new component opens immediately the properties editor. To edit a component, click the Edit icon on the right.
The properties of a wall component are:
- Function: each component has its own function which can define its behavior and appearance. The available functions are: Exterior and Interior Finish, Thermal Film, two kinds of Thermal Insulation, Air Layer, Substrate, Structural, Membrane. There can only be one exterior and one interior finish. The (batting) Thermal insulation component is always rendered with the Insulation line type.
- Thickness, in the current drawing units;
- Fill color, hatch, hatch color and hatch scale.
Click the Cancel ✖ or OK ✔ buttons to cancel or confirm the changes to a component and return to the list of components. The + button confirms the current component and creates a new one.
Construct and Edit Walls
Construct and Edit Walls
To draw a wall, click to set its start point, move the cursor and click again to set its endpoint: walls are connected like poly-lines. Walls have their construction side and the “Exterior side” property, marked with a blue line, to consider when inserting openings: to change the leading side while drawing, click on the Option menu close to the last vertex. Press the Alt key to invert the exterior side while moving the cursor.
A compound wall can be inserted by its structural component: choose between exterior, interior sides and middle line to easily align your walls to the structural grid.
To edit a wall, select it and move, stretch, shorten it with the Arrow tool or change its parameters numerically via the Object Info panel.
Edit a Wall with the Object Info Panel
The Point section of the Object Info panel enables the changes of the coordinates of the three control points of the selected wall: use the arrows to select the active point and the fields to enter the new coordinates.
The Geometry section displays the following options:
- Length and Width fields to change its geometry;
- Leading side buttons to change the construction axis of the wall (this option can shift the selected wall accordingly);
- Invert Sides to invert Interior/Exterior side of the wall (this can invert the opening direction of windows and doors inserted in the selected wall).
The ID section shows the wall Name, Tag and Description fields to add information to the selected wall and provides the Settings button to open the Wall Settings window.
The Tools menu and the contextual menu provide two commands specific for walls: Convert to Wall and Rebuild Wall.
Standard-Case Walls
Standard-case walls have one uniform component and its representation can be a solid color fill, a hatch, or a combination of the two. The geometry can be rectangular, with a constant thickness from start to end point, or polygonal, with variable thickness from start to end.
_
Basic walls automatically join to other basic walls, regardless of thickness and fill, unless the joints are disabled in the Settings window.
Standard-Case Wall Settings Window
- Type pop-up window and New Type icon.
- Family, Basic or Compound
- Geometry and Thickness, in the current unit: selecting the option of variable thickness enables the end thickness field.
- Leading side and Exterior side: select the construction side of the wall. You can also access this option by clicking the pop-up menu icon during the construction the wall. The option to invert the interior and exterior faces of the wall allows to switch the sides of the wall. The exterior side is highlighted in blue when drawing and selecting walls. Wall Joints options. Deselect an option to disable the automatic connection of new walls or to unlink an existing wall.
- Border attributes: Line type and pen weight.
- Fill attributes: solid color, hatch type and color, hatch scale.
Utilities for Walls
Convert to Wall
Convert To Wall applies to lines, polygons, arcs and curves. This function converts those objects into walls with the current settings: select the items to convert and then choose Tools ▸ Walls ▸ Convert To Wall on the Tools menu. This command is also available as a button in the Edit Tool Bar.
Rebuild Wall
Use this command to regenerate the geometry, side intersections and nodes of one or more walls. This is especially useful in situations in which a node needs to fixed.
The Rebuild Wall tool can either be applied to selected walls, or to multiple walls in one run by clicking on them.
To use it on the selection:
- Select the walls you want to rebuild;
- Choose Tools ▸ Rebuild Wall or open the radial menu and choose Rebuild Wall fromthe Tools submenu.
To apply it to multiple walls:
- Choose Tools ▸ Rebuild Wall or open the radial menu and choose Rebuild Wall from the Tools submenu.
- Click once on each wall to rebuild
- Click on a void part or on another object to end.
Wall Tool Settings
Walls are parametric elements of the building that can have several different properties such as sizes, options, functions and compositions that define a wall type. Use the Wall tool settings window to define the parameters of the wall type.
_
Wall Family
You can select to create a standard-case (basic) wall or a composite wall.
Standard-case Walls
When you select standard-case walls, you can select its geometry as regular or irregular. Regular walls are defined by one thickness value and their shape in plan view is rectangular.
Irregular walls are defined by start and end thickness values.
Basic walls automatically join to other basic walls, regardless of thickness and fill, unless the joints are disabled in the Settings window.
Composite Walls
Composite walls consist of multiple layered components, each with its own properties. Composite walls can only be rectangular in shape, with constant thickness from start to end. The total thickness is calculated as the sum of all the internal components.
_
When you select the Composite Wall family in the Settings panel, the family-specific section shows a button to edit the internal components, the value of the total thickness calculated as the sum of the internal components, and the pen wight menu to define the pen to be used for the lines that separate the internal components.
- Composite walls can have any number of internal components, and you can add, remove, reorder and edit the components at any time through the Wall Components window.
- By default, basic walls and compound walls do not join automatically, because they are different elements that would not be joined in a real situation. Also, they are made of different materials which would not match. However, if a particular situation requires it, you can choose to activate the Allow Joints options and attempt to join two walls of different type.
_
Editing Composite Wall Components
Press the Edit button on the Wall tool settings window to open the Wall Components panel. This panel allows you to define, reorder and edit the internal components of the current wall type.
_
The table lists the components of the wall from the exterior side to the interior, with a progressive index number. The selected component is highlighted in the preview, which shows the current wall at the scale. You can check how the wall is rendered at the different drawing scales by using the drawing scale menu on the preview area.
The total thickness of the wall is computed on the sum of the single components and shown at the bottom of the Thickness column.
You can add, remove and reorder the components, and rename a component by double-clicking its name. Use the + button to add a new component and the - button to remove the selected component in the table. Adding a new component opens immediately the properties editor. To edit a component, click the Edit icon on the right.
Use Component panel to enter the component name, function, thickness and the hatch to be used in horizontal and vertical sections.
Click the Cancel ✖ or OK ✔ buttons to cancel or confirm the changes to a component and return to the list of components. You can also push the + button to confirm the current component and create a new one directly without going back to the components list.
Windows
Subsections of Windows
About Windows
Windows are architectural elements that belong to the Openings class and in their most basic function are used to open holes in walls. Openings are hosted elements in that they can only be placed in a wall, that acts as the host element.
Like any other architectural element, windows have geometric, graphic and information parameters that you can edit through the settings window and the Object Info panel.
Topics in this Section
- Window tool settings
- Insert a Window
- Editing a Window
Editing a Window
You can resize, move and flip a window directly by clicking one of its control points. All editing operations are available when the window is selected, but the flip operations are only available when the window is the only selected object.
Resize a Window
To resize a window, click one of its handles at the start or end sides and move the pointer. Pop-up dimensions show the current size. You can enter a new size value or click to end the editing operation.
Move a Window
Click its middle handle to move the window within its wall.
Flip a Window
Click the double arrows to flip the opening direction, outside or inside.
Editing a Window with the Object Info Panel
The Geometry section displays the Rough Width and Nominal Width fields to change the size of the selected window.
The ID section shows the Name, Tag and Description fields to edit or add information to the selected window: use the Settings button to open the Window Settings dialog.
The Opening Direction of a window can be changed through the Settings window: select the window, open the Options pane of Settings and select Opening Direction > “Open Inside” or “Open Outside”.
Insert a Window
To insert a window in a wall, activate the Window tool in the Toolbox and do the following:
- In the Settings window load the Type if available or select the family of the opening;
- Enter the desired window settings;
- In the Project window set the position of the opening by clicking on the wall;
- Click the internal / external area of the wall to choose the opening direction.
As you move the cursor over a wall, temporary dimensions show the relative distances of the opening from the surrounding vertices or joints of the wall.
To set and constrain the value of either dimension, so that the opening is exactly at that distance from a reference point, enter the value on the keyboard and move the pointer, so as to choose which dimension on either side of the wall the value applies to. Click to confirm and insert the opening.
NOTE Windows are always inserted relative to the external surface of the wall, which is marked in blue when selected.
Window Tool Settings
To open the tool settings of windows, select Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Window… or double-click the tool icon. You can load an existing Window Type if available or customize the window by selecting its family and setting all the parameters and options. Current settings can be saved as new types by pressing the Add icon.
The Window tool settings window includes two panels: Geometry and Options.
_
Window Geometry
Use this panel to configure the parameters that define the shape and size of the window, such as width, height, reveal type, etc. The panel is provides the following options:
- Family. Open the drop-down menu to select the window family from the list. The available families include:
- empty opening
- generic and simple windows, symbolic representations of a window
- casement windows
- single/double -hung windows
- sliding windows
_
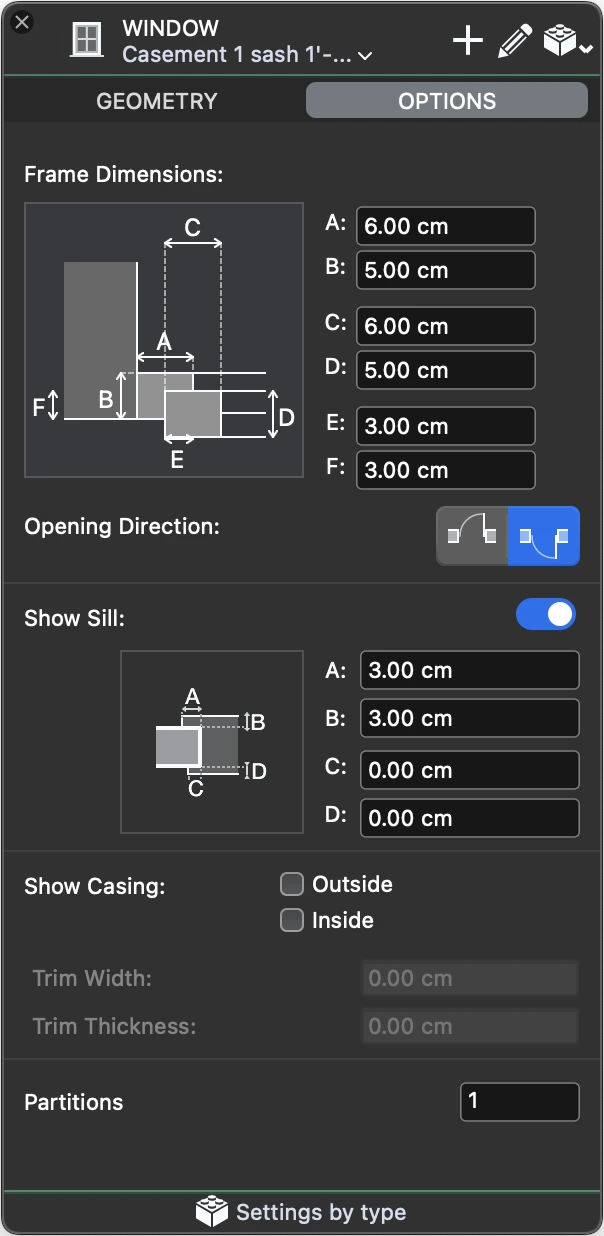
Window Options
Use this panel to specify the dimensions of the frame, opening directions, the optional sill and various display options.
Window Options
Use this panel to specify the dimensions of the frame, opening directions, the optional sill and various display options.
- Frame Dimensions. Depending of the current reveal, you can specify the dimensions of the various components of the door frame.
- Opening Direction, outward or inward.
- Show Sill. Activate the switch to enable the controls and define external and internal offsets and widths of the sill.
- Show Casing. Depending on the desired level of detail, you can choose to display the outside and inside casing component and specify its dimensions.
- Partitions: specify the number of internal partitions of the window.